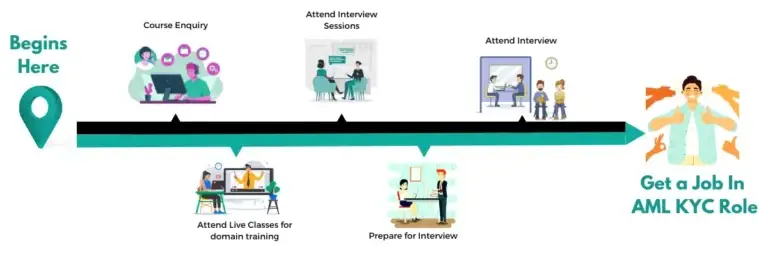
Data Science Interview Questions Data Science Interview Questions 1. What...
Read MoreAI & Machine Learning in AML Monitoring
Last Updated on Feb 17, 2026, 2k Views
AI & Machine Learning in AML Monitoring
AI & Machine Learning in AML Monitoring
Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) are transforming Anti-Money Laundering (AML) monitoring by making systems smarter, faster, and more accurate. Traditional rule-based systems often generate high false positives and struggle to detect evolving financial crime patterns. AI-driven AML solutions address these limitations with advanced analytics and predictive modeling.
Why AI is Important in AML Monitoring
Financial institutions face increasing regulatory pressure from global bodies like the Financial Action Task Force (FATF) and must comply with local regulations such as:
Prevention of Money Laundering Act (India)
Bank Secrecy Act (USA)
Traditional monitoring systems:
Depend on static rules
Require manual threshold tuning
Generate excessive false alerts
Struggle with complex transaction patterns
AI enhances AML programs by enabling real-time, risk-based monitoring.
Key Applications of AI & ML in AML
1. Transaction Monitoring Optimization
Machine learning models analyze historical transaction data to:
Identify unusual patterns
Detect anomalies in customer behavior
Reduce false positives
Prioritize high-risk alerts
Unlike rule-based systems, ML adapts to new typologies without constant manual updates.
2. Customer Risk Scoring
AI improves KYC and CDD by:
Dynamically assessing customer risk profiles
Incorporating behavioral analytics
Using predictive modeling to detect high-risk customers early
This supports risk-based approaches recommended by global regulators.
3. Suspicious Activity Detection
Supervised learning models are trained on previously filed Suspicious Activity Reports (SARs) to:
Predict suspicious transactions
Identify layering and structuring patterns
Detect mule accounts and synthetic identities
4. Network & Graph Analytics
AI-powered graph databases map relationships between:
Individuals
Shell companies
Cross-border accounts
This helps uncover hidden networks involved in trade-based money laundering, terrorist financing, and fraud.
5. NLP for Adverse Media Screening
Natural Language Processing (NLP) tools:
Scan global news and sanctions lists
Identify negative news related to customers
Automate name screening processes
AI reduces manual compliance workload significantly.
Types of Machine Learning Used in AML
Supervised Learning
Uses labeled historical data
Effective for SAR prediction
Examples: Logistic regression, Random forests, Neural networks
Unsupervised Learning
Detects anomalies without labeled data
Useful for new typologies
Examples: Clustering, Isolation Forest
Semi-Supervised Learning
Combines both approaches
Useful when labeled data is limited
Benefits of AI in AML Monitoring
✔ Reduced false positives
✔ Faster investigations
✔ Better risk prioritization
✔ Enhanced detection accuracy
✔ Real-time monitoring capabilities
✔ Cost efficiency in compliance operations
Challenges of AI in AML
Data quality issues
Model explainability (regulatory concern)
Bias and fairness risks
Integration with legacy systems
High implementation costs
Regulators increasingly expect explainable AI models rather than “black-box” systems.
Future Trends in AI-Driven AML (2026 & Beyond)
AI-powered regulatory reporting automation
Federated learning for privacy-preserving AML collaboration
Integration of blockchain analytics
Real-time cross-border monitoring systems
Explainable AI (XAI) frameworks for audit transparency
Conclusion
AI and Machine Learning are reshaping AML monitoring by moving beyond static rule-based systems toward intelligent, adaptive compliance frameworks. While challenges remain, AI adoption is becoming essential for financial institutions to stay compliant, competitive, and resilient against increasingly sophisticated financial crimes.
Career Advice!
Feel Free to Contact Us or WhatsApp Us for Career Counseling!
- +91 9066508122
Top 30 DevOps Interview Questions & Answers (2022 Update)
Top 30 DevOps Interview Questions & Answers (2022 Update) Top...
Read MoreAnti Money Laundering Interview Questions
Anti Money Laundering Interview Questions Anti Money Laundering Interview Questions...
Read More